Auction Market Theory: Decoding Market Behavior
Introduction to Auction Market Theory
Auction Market Theory (AMT) is a powerful philosophy that has revolutionized the way traders and investors analyze financial markets. At its core, AMT provides a framework for understanding how markets operate as continuous two-way auctions, with buyers and sellers interacting to determine prices.
This article delves into the various aspects of AMT and explores key concepts and applications that make it an invaluable tool in financial analysis.
Auction Theory: A Simple Explanation
Auction theory is the study of how buyers and sellers interact in auction markets to determine the price and allocation of goods or assets. In its simplest form, auction theory examines the rules governing auctions, the behavior of participants, and the resulting outcomes.
Bidders: Participants who make offers to buy the goods being auctioned.
Sellers: Participants who present the goods for sale at the auction.
Auctioneer: The entity responsible for conducting the auction and facilitating transactions.
The Pioneers of Auction Theory
Auction theory has been shaped by the contributions of several key figures, each bringing unique insights to the field:
Paul Milgrom: An economist known for his pioneering work in auction theory and the design of complex auctions. Milgrom's research has had a profound impact on auction design for industries such as telecommunications.
Jim Dalton: A renowned trader and educator who contributed to the development of AMT. Dalton emphasized the use of market profile analysis to understand market behavior.
Types of Auction Theory
There are several types of auction theory that describe different auction mechanisms:
English Auction: Also known as an open ascending price auction, where bidders openly bid against each other, and the highest bidder wins.
Dutch Auction: An open descending price auction, where the auctioneer starts with a high price and gradually lowers it until a bidder accepts the price.
First-Price Sealed-Bid Auction: Bidders submit sealed bids and the highest bidder wins, paying the price they bid.
Vickrey Auction: A sealed-bid auction where the highest bidder wins but pays the second-highest bid price.
Volume Profile Auction Market Theory
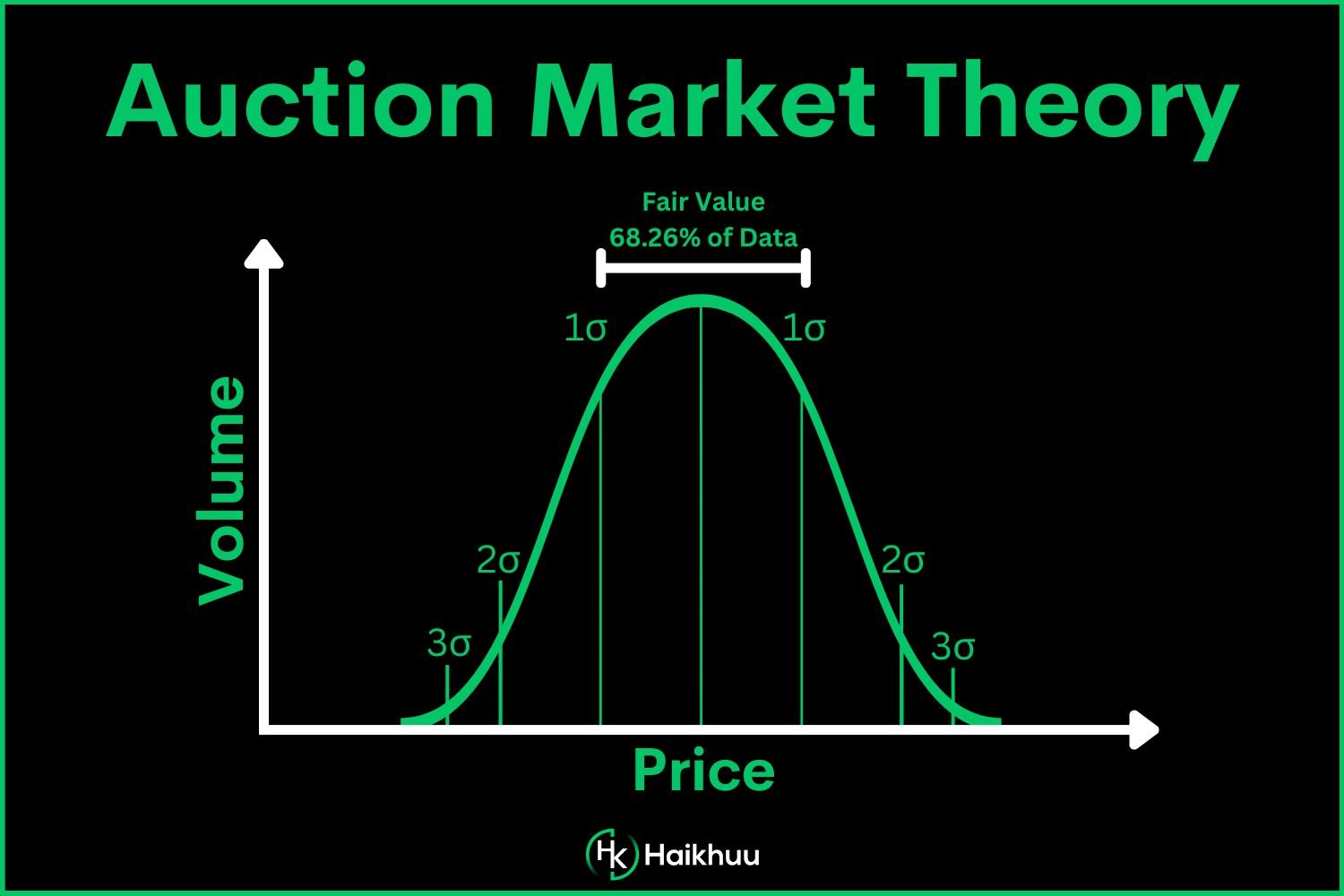
Volume profile is a key component of AMT that represents the distribution of trading volume at different price levels over a specified period. It provides insights into:
Value Area: The price range where a majority of the trading volume occurred. It represents the area of fair value where buyers and sellers agree on price.
Point of Control (POC): The price level with the highest trading volume. It is seen as the focal point of market activity.
Auction-Based Models
Auction-based models are mathematical representations of auction markets. These models help analyze and predict market behavior based on various factors such as bidding strategies, auction rules, and market conditions. Auction-based models are used in fields like finance, economics, and game theory to study market dynamics and design optimal auctions.
Jim Dalton's Auction Market Theory
Jim Dalton's approach to AMT emphasizes the significance of market profile analysis—a graphical representation of price, time, and volume—to understand market behavior. Dalton's AMT focuses on:
The concept of balance and imbalance in markets.
The role of value area and POC in identifying trading opportunities.
The Principles of Auction Market Theory
AMT is guided by a set of fundamental principles:
Balance: Markets are in balance when buyers and sellers agree on price, leading to a range-bound market.
Imbalance: Markets are imbalanced when one side (buyers or sellers) becomes dominant, resulting in price movements and trends.
Value Area in Auction Market Theory
The value area is a crucial element of AMT analysis. It represents the price range where most trading activity occurs, signifying a consensus of fair value among market participants. Within the value area:
Buyers and sellers find common ground on price, leading to balanced market conditions.
Prices are deemed acceptable and reasonable by the majority of participants.
Understanding the value area helps traders identify potential support and resistance levels and areas of opportunity for potential price breakouts.
Benefits and Limitations of Auction Market Theory
AMT offers several benefits to traders and market analysts:
Enhanced Market Understanding: AMT provides a logical framework for interpreting market behavior and price movements.
Informed Decision-Making: By identifying areas of balance and imbalance, traders can make informed decisions about entry and exit points.
Insight into Market Dynamics: The use of volume profile and market profile analysis offers valuable insights into market dynamics and participant behavior.
However, AMT has limitations to consider:
Reliance on Observation: AMT is based on observing market behavior, and predicting future price movements remains challenging.
Complementary Analysis: AMT is most effective when used in conjunction with other market analysis techniques, such as technical and fundamental analysis.
Auction Market Theory | Bottom Line
Auction Market Theory is a valuable tool for understanding the intricacies of financial markets. By viewing markets as continuous two-way auctions, AMT offers insights into the behavior of buyers and sellers and the factors that influence price movements.
Whether used to identify areas of opportunity or to gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics, AMT has earned its place as a fundamental component of modern financial analysis. As markets continue to evolve, the principles of AMT will remain relevant, guiding traders and investors toward informed and strategic decision-making.