VUG vs. QQQ | Vanguard Growth vs. Nasdaq ETFs
This article compares VUG and QQQ ETFs, analyzing their historical performance, differences, and which may be best for your portfolio.
Key Takeaways
VUG and QQQ are both ETFs that track the performance of the U.S. stock market, but they have different compositions and strategies.
VUG tracks the CRSP US Large Cap Growth Index, which includes large-cap U.S. growth stocks, while QQQ tracks the NASDAQ 100 Index, which includes 100 of the largest non-financial companies listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange.
VUG may be a better option for investors seeking exposure to large-cap growth stocks, while QQQ may offer more diversification across the technology sector.
Both funds have relatively low expense ratios and are good long-term investment options.
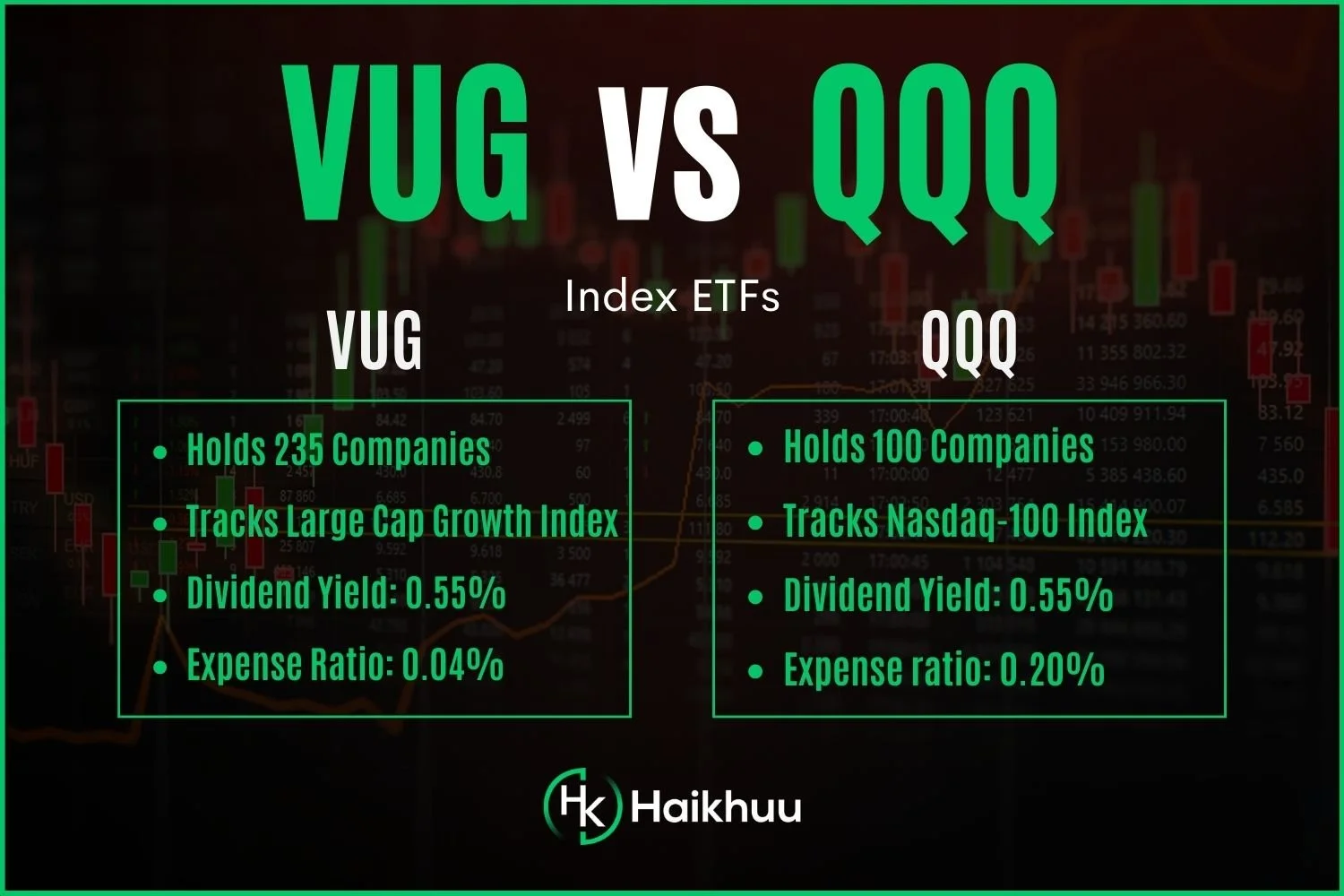
VUG (Vanguard Growth ETF) vs. QQQ (Nasdaq ETFs)
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are popular investment vehicles that offer investors exposure to a diversified portfolio of securities. VUG and QQQ are two of the most popular ETFs in the market.
VUG, or Vanguard Growth ETF, tracks the performance of the CRSP US Large Cap Growth Index, including companies with higher expected earnings growth rates.
QQQ, or the Nasdaq ETF, tracks the performance of the Nasdaq-100 Index, which includes the largest non-financial companies listed on the Nasdaq Stock Market.
While both VUG and QQQ are growth-oriented ETFs, there are essential differences between the two in terms of their holdings, expense ratios, historical performance, and other factors.
As such, investors must understand these differences to make informed investment decisions and determine which ETF best suits their portfolio and investment goals.
VUG Details
Expense Ratio: 0.04%
Dividend Yield: 0.68%
10yr Return: 13.44%
VUG has a low expense ratio of 0.04%, which is significantly lower than the average expense ratio of actively managed mutual funds. Additionally, VUG has no front-end or back-end loads, making it a cost-effective investment option for investors seeking exposure to large-cap growth stocks.
QQQ Details
Expense Ratio: 0.20%
Dividend Yield: 0.70%
10yr Return: 16.20%
QQQ has an expense ratio of 0.20%, slightly higher than VUG's expense ratio. However, this expense ratio is still significantly lower than the average expense ratio of actively managed mutual funds. QQQ has no front-end or back-end loads, making it a cost-effective investment option for investors seeking exposure to large-cap technology and biotechnology companies.
VUG vs. QQQ Historical Performance
Over the long-term, both VUG and QQQ have delivered strong returns to investors. However, there are some differences in their historical performance. For example, from 2016 to 2020, QQQ outperformed VUG, with an average annual return of 26.8% compared to VUG's average annual return of 23.2%. However, from 2011 to 2015, VUG outperformed QQQ, with an average annual return of 16.1% compared to QQQ's average annual return of 14.6%.
VUG and QQQ have also performed differently in various market conditions. For example, during the technology bubble of the late 1990s, QQQ significantly outperformed VUG. However, during the market downturn that followed the bubble's collapse, VUG outperformed QQQ. In recent years, QQQ has performed particularly well during periods of strong growth in the technology sector, while VUG has performed well during periods of broader market growth.
VUG vs. QQQ Differences
The main difference between VUG and QQQ is how many companies each fund owns. VUG owns over 250 companies, while QQQ only holds 100. Therefore, VUG is more diversified and will offer more protection during drawdowns.
The differences between VUG and QQQ can have a significant impact on investment decisions. For example, investors looking for exposure to the technology sector may prefer QQQ due to its heavier allocation to this sector. On the other hand, investors who are looking for a more diversified growth-oriented ETF may prefer VUG.
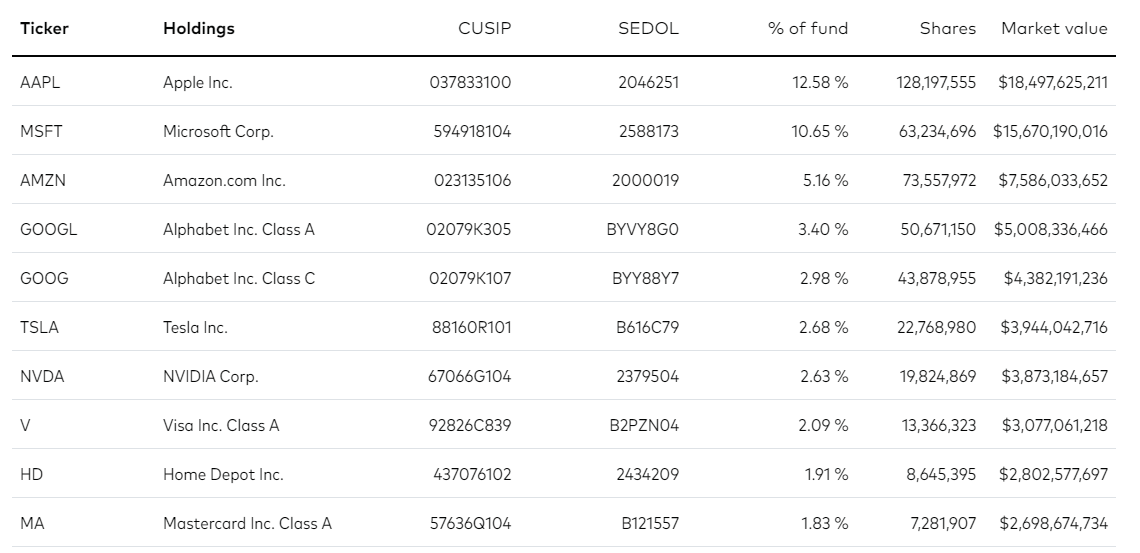
VUG Holdings
QQQ Holdings
VUG vs. QQQ | Which is Best for Your Portfolio?
When deciding between VUG and QQQ, investors should consider several factors, including their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and overall portfolio composition. For example, VUG may be a good option if your portfolio lacks growth stocks.
Investors will take slightly more risk investing in QQQ, which may be good depending on the rest of your investment portfolio. For example, if you only hold value stocks and ETFs, adding a more volatile ETF like QQQ is an excellent way to improve your portfolio's return potential.