VTV vs. VTI: Which Vanguard ETF Is Better?
This article will compare the Vanguard ETFs VTV and VTI, exploring key characteristics, performance metrics, risk analysis, and more.
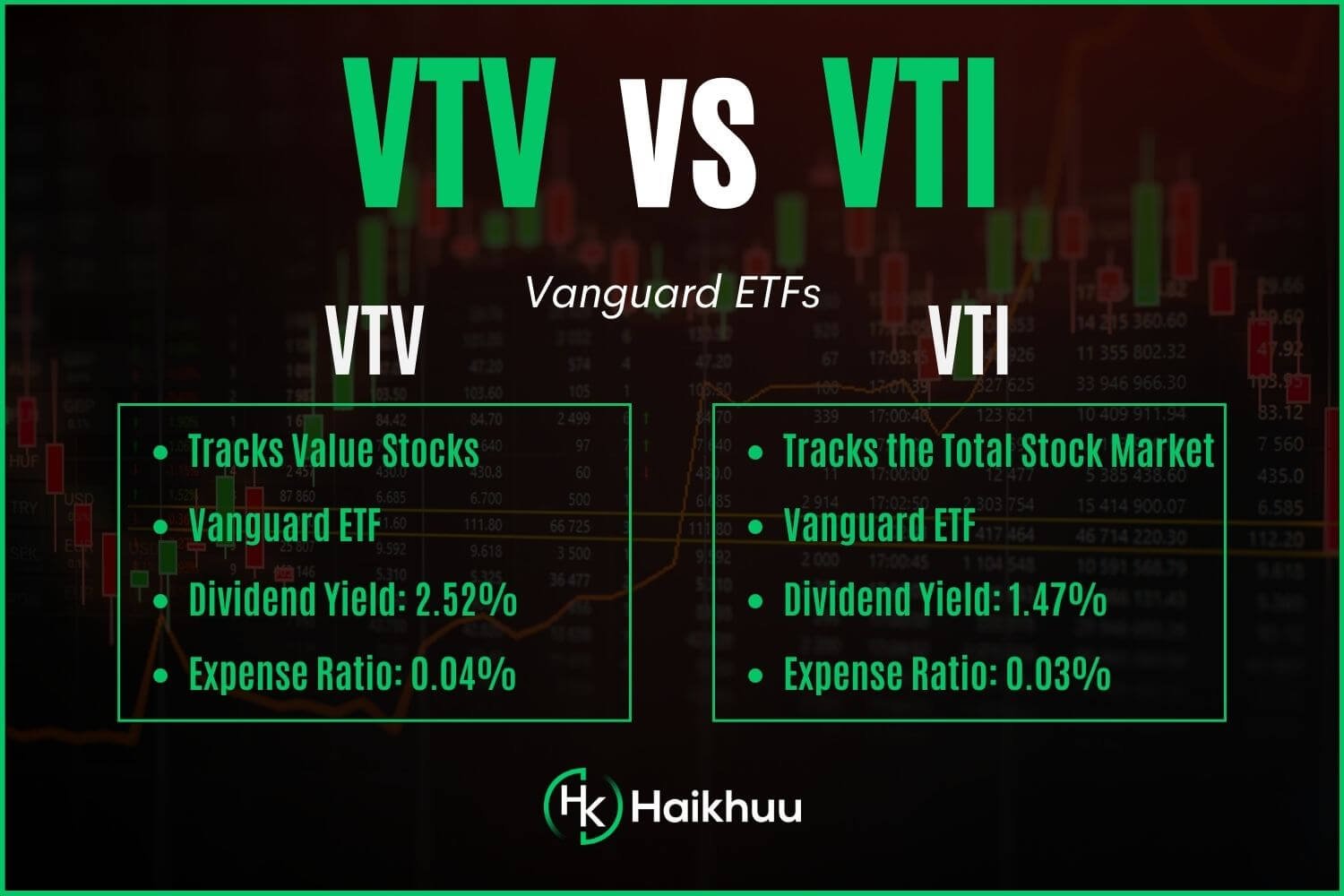
Vanguard Value ETF (VTV) and Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI) Overview
VTV and VTI are both passively managed Vanguard ETFs, seeking to mimic the performance of their respective indices. VTV, launched in 2004, tracks the MSCI US Prime Market Value Index and aims to represent the performance of US large- and mid-cap companies indicating value characteristics.
On the other hand, VTI, which was put on the market in 2001, tracks the performance of the CRSP US Total Market Index, encompassing the entire U.S. stock market.
VTV vs. VTI: Performance Comparison
As per market dynamics, the performance of VTV and VTI depends on several factors, mainly whether the market is bullish or bearish.
VTI gives exposure to the entire U.S. stock market, so it tends to be more balanced and may perform well in most market conditions.
On the other hand, VTV, being tilted towards value stocks, might outperform when the market is bearish or flat, since its holdings pay more dividends and are less volatile.
VTV vs. VTI: Dividend Comparison
VTV - 2.52%
VTI - 1.47%
Both ETFs pay dividends, but VTV pays a higher yield than VTI. As value stocks often have higher dividend yields, investors aiming for income might find VTV more appealing.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to remember that investing solely based on dividends can risk missing out on potential growth supplied by non-dividend-paying stocks featured in VTI.
VTV vs. VTI: Expense Ratio Comparison
VTV - 0.04%
VTI - 0.03%
Expense ratios, or the fees charged to manage a fund, are another crucial factor to consider.
Being passive index ETFs, both VTV and VTI feature low expense ratios. VTI has a slightly lower expense ratio, but both funds are much lower than the average.
Therefore, it is best not to worry too much about the expense ratio when comparing these funds since they are both excellent deals and low-cost.
VTV vs. VTI: Holdings Comparison
VTI holds a comprehensive and diversified portfolio, covering the entire U.S. stock market, which encapsulates over 4000 stocks. This warrants extensive diversification and exposure to various industries and companies of all sizes.
Conversely, VTV, while still diversified, is less so than VTI, with its portfolio concentrated around 340 large and mid-cap U.S. value stocks.
The main difference between the holdings of VTV and VTI is that VTV solely focuses on value companies while VTI invests in the total stock market.
VTV vs. VTI: Correlation
Both ETFs have shown an extremely high correlation over the past few years, as they both generally consist of the same segment of stocks – U.S. equities.
A high correlation means that the two funds move in the same direction and at similar magnitudes, offering almost no risk diversification when holding both in the same portfolio.
VTV vs. VTI: Risk Analysis
Risk and reward are two sides of the same coin in investments. With their exposure to U.S. equities, both VTV and VTI represent similar market risk levels. However, the value focus could make VTV more susceptible to underperform during the periods when growth outperforms, constituting additional systematic risk.
In conclusion, choosing between VTV and VTI is dependent on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and market outlook. Both ETFs have their strengths; VTV for capturing the value premium, and VTI for benefiting from the entire U.S. stock market growth.
If you want to learn more about investing in the stock market, you can join the HaiKhuu Trading Community.
HaiKhuu offers live trading calls, daily morning reports, and an awesome community of like-minded traders to learn from.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
1. Will VTV outperform VTI?
VTV might outperform VTI during periods when value stocks perform particularly well. Conversely, VTI could have the upper hand when the broader market outperforms the value index. Hence, the performance discrepancy between VTV and VTI is implicitly associated with the market’s preference for value or growth stocks.
2. Is VTV better than Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO)?
It depends on an individual’s investment objectives. VTV offers exposure to value stocks, while VOO provides a broad market representation by tracking the performance of the 500 largest U.S. firms. Therefore, VTV might be a better fit for investors seeking to capture the value premium, while VOO could be suitable for those desiring broad market exposure.