VUG vs. VTI - Which is Best For You?
In the family of Vanguard ETFs, two popular choices often come under the spotlight are the Vanguard Growth ETF (VUG) and the Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI).
Key characteristics of VUG and VTI
VUG has a higher expense ratio
VUG will likely outperform in bullish markets
VTI holds many more companies than VUG
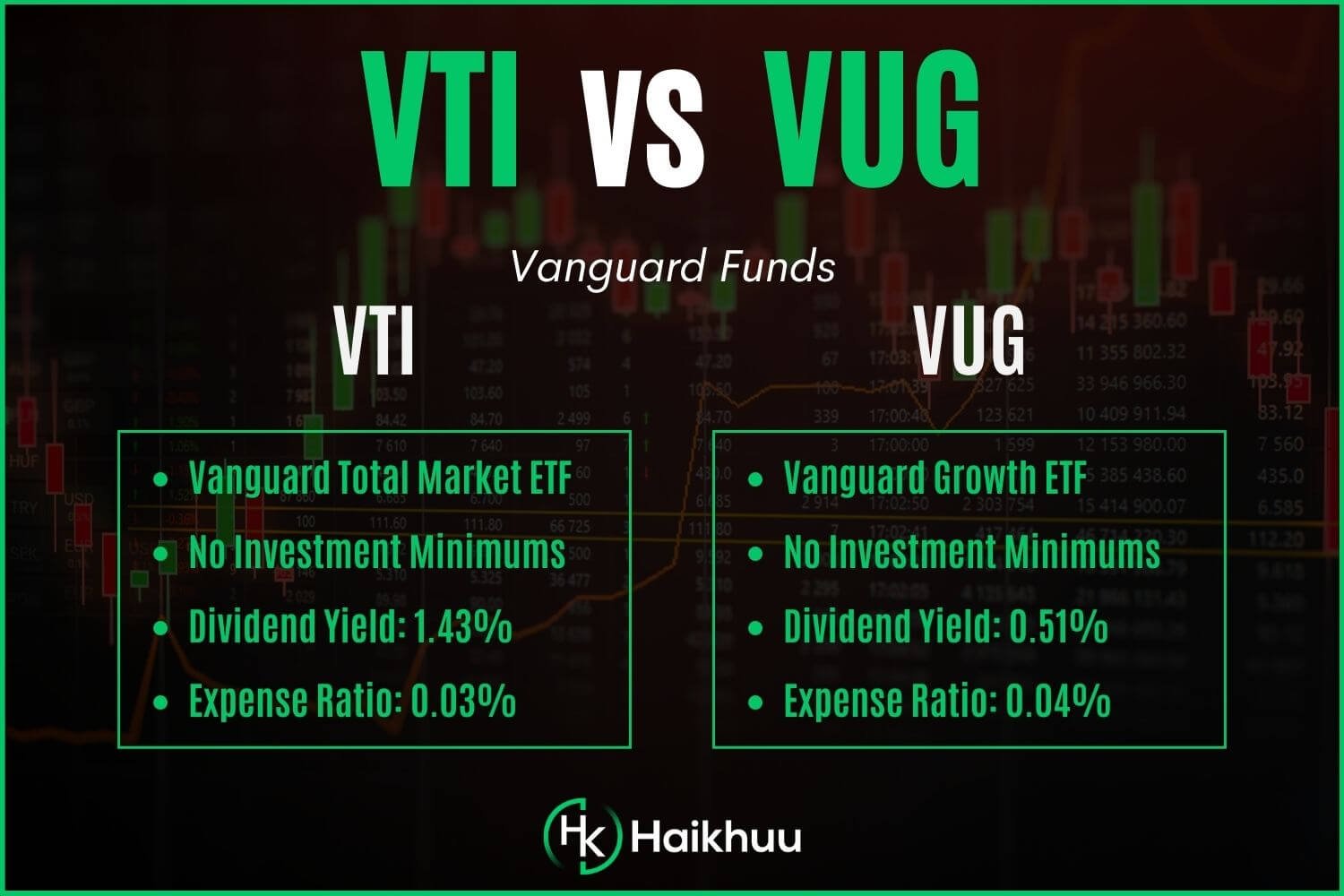
VUG is an exchange-traded fund passively managed by Vanguard that tracks the CRSP U.S. Large Cap Growth Index, exposing investors to large U.S. firms projected to grow faster than other stocks.
On the other hand, VTI tracks the CRSP US Total Market Index, which covers virtually every company in the entire U.S. equity investment universe.
Correlation between VUG and VTI
Given that both VUG and VTI are based on U.S. stocks, they tend to move in the same direction with economic cycles and market movements.
However, VUG, being a growth fund, may show enhanced sensitivity to market ups and downs compared to the more diversified VTI.
Performance comparison of VUG and VTI
A performance comparison of VUG and VTI reflects similar trends, given the correlated nature of U.S. market equity investments.
Since VUG focuses on growth equities, it generally performs well during bullish markets when growth stocks surge.
On the contrary, VTI, with its broad market exposure, cushions the downturn during bearish markets.
Dividend comparison of VUG and VTI
VTI has a higher dividend yield than VUG since it doesn’t focus solely on growth companies that are less worried about paying high dividend yields.
The dividend yield of VUG is around 0.51%, which reflects its allocation to growth businesses that prefer to reinvest in the business rather than return cash to shareholders.
VTI, with a multitude of companies, offers a higher dividend yield of 1.30%, appealing to income-focused investors.
Expense ratio comparison of VUG and VTI
VUG - 0.04%
VTI - 0.03%
Vanguard is known for its low-cost offerings. Both VUG and VTI boast low expense ratios, which pass on more of the fund’s return to the investors.
VUG has an expense ratio of 0.04%, only slightly higher than VTI’s expense ratio of 0.03%.
VUG vs. VTI - Bottom Line
Both VUG and VTI offer different advantages for different types of investors. VUG focuses on growth and may benefit investors looking for potential return acceleration.
In contrast, VTI offers broad exposure to the U.S. equity market, suitable for investors aiming for diversification and a more balanced risk-reward outlook.
If you want to learn more about investing in the stock market, you can join the HaiKhuu Trading Community.
HaiKhuu offers live trading calls, daily morning reports, and an awesome community of like-minded traders to learn from.