SPY vs. VOO - A Comprehensive Comparison
Key Characteristics of SPY and VOO
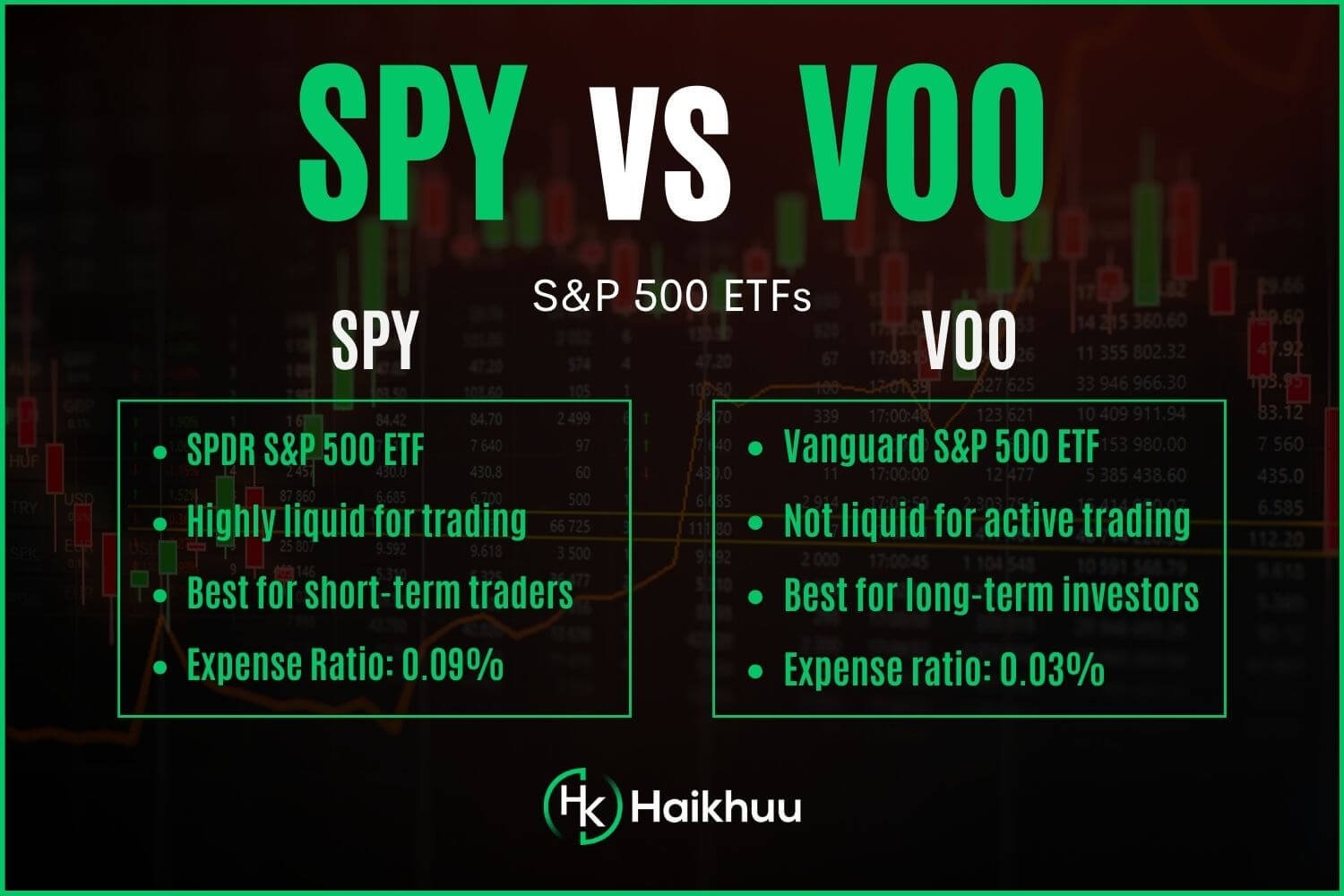
What Are They? - SPY and VOO are exchange-traded funds (ETFs) designed to provide investors with a return that tracks the performance of the S&P 500 - one of the world’s best benchmarks for U.S. equities.
Snapshot Comparison - Launched by State Street in 1993, SPY is the elder statesman of the ETF world. VOO, on the other hand, only started trading in 2010 but has grown rapidly thanks to Vanguard’s sterling reputation for low-cost offerings.
The Main Difference - The biggest difference between SPY and VOO is liquidity. SPY is the most liquid ETF available for both equity and options. VOO is much less liquid, and the options are not liquid enough for active trading.
Expense Ratio Comparison
One of the major distinguishing factors between the VOO and SPY is their management expense ratios.
VOO’s annual expense ratio stands at 0.03%. In contrast, SPY posts a higher expense ratio of 0.09%.
Over a long investment horizon, VOO’s lower expense ratio could save investors significant money.
Performance Comparison: SPY vs. VOO
When comparing performances (never forgetting past performance is no guarantee of future results), both ETFs tend to track their respective index closely.
However, the slightly lower expense ratio of VOO usually lends itself to a slightly better performance over long periods, particularly in a growing market.
A Look at Dividends: SPY vs. VOO
The dividend yield of VOO is around 1.49%, while the dividend yield of SPY is 1.46%.
VOO historically has had a slightly higher yield than SPY. For income-focused investors, this might tip the scale in favor of VOO.
However, the difference is negligible and is not that important when choosing between VOO and SPY.
Risk-Adjusted Performance Comparison
The risk-adjusted performance, often characterized by the Sharpe Ratio, enables investors to understand the fund’s risk-reward tradeoff.
Although both ETFs have virtually identical market risk (beta), the slight variation in returns due to cost differences can result in a higher Sharpe ratio for VOO, indicating better risk-adjusted returns.
Correlation Between SPY and VOO
Both SPY and VOO are based on the S&P 500 Index, which means they have a high degree of correlation. When the S&P 500 goes up or down, you can expect both SPY and VOO to also move in the same direction, usually to a similar degree.
However, precisely because they have different expense ratios and slightly different portfolio holdings, their returns may not be exactly the same.
VOO vs. SPY - Which is Best For You?
So, which one is better? Well, from a purely cost and performance standpoint, VOO has a slight edge due to its lower expense ratio and higher dividends for investors. Therefore, VOO is the best option for long-term investors.
However, SPY has its benefits, too - it has established more liquidity, and it allows for more flexibility in trading methods, such as options. Additionally, the expense ratio is still very low, making SPY suitable for long-term investors and traders.
Therefore, if you are a long-term investor, VOO is best for you, while SPY is best for short-term traders.
If you want to learn more about investing in the stock market or active trading, you should join the HaiKhuu Trading Community! HaiKhuu offers live trading calls, daily morning reports, and is a friendly community of traders and investors willing to help you learn!
FAQ: Understanding SPY and VOO
Is there a difference between SPY and VOO?
Yes, there is a difference between SPY and VOO, even though they both track the S&P 500 Index. The key differences lie primarily in their expense ratios, dividend yields, and inception dates. SPY, managed by State Street, is older and has an expense ratio of 0.09%. VOO, managed by Vanguard, maintains a lower expense ratio of 0.03%.
Why is SPY more popular than VOO?
SPY is more popular because it was the first ETF ever to exist, having been established in early 1993. It has built up a reputation and has developed substantial liquidity and trading volume over the years. However, in terms of assets under management, VOO has caught up, indicating its growing popularity.
Should I invest in both VOO and SPY?
Investing in both may seem redundant, given that both track the same index. However, some investors may choose to do so to take advantage of the slightly different performances and costs associated with each ETF. Ultimately, the decision depends on your personal investment objectives, risk tolerance, and preference.
Is it wise to invest in VOO?
Investing in VOO is generally considered a wise move for long-term investors seeking exposure to the U.S. equity market. Vanguard’s renowned low-cost structure helps maximize returns over time. That said, investors should always research thoroughly and consider their personal financial goals before investing.
What are the primary differences between VOO and SPY?
The primary differences between VOO and SPY are the expense ratios and the dividend yields. VOO typically has lower costs and a slightly higher dividend yield compared to SPY.
Which ETF has a better performance, SPY or VOO?
While both VOO and SPY aim to track the S&P 500 Index, the lower expense ratio of VOO can lead to slightly better performance over time. This can make a noticeable difference for longer-term investments, given the compounding effect.