VT vs. VTI | The Best Total Stock Market ETFs
VT and VTI are broad market ETFs, but they have some differences investors must be aware of before investing.
Key Takeaways
VT and VTI are both ETFs that track the performance of the global stock market, but they have different compositions and strategies.
VT tracks the FTSE Global All Cap Index, which includes large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks from developed and emerging markets around the world, while VTI tracks the CRSP US Total Market Index, which includes nearly all U.S. stocks.
VT may be a better option for investors seeking global diversification, while VTI may be a better option for those seeking exposure to the U.S. stock market specifically.
Both funds have relatively low expense ratios and are good long-term investment options.
VT (Vanguard Total World) vs. VTI (Vanguard Total Stock)
VT and VTI are broad market ETFs that invest in thousands of stocks to provide investors with overall exposure to the entire stock market. VTI holds nearly 4,000 stocks, while VT holds around 9.500 companies.
VT invests in all types of companies, including emerging markets and foreign stocks. On the other hand, VTI only invests in American companies, which is the main difference between the two.
VT Details
Expense Ratio: 0.07%
Dividend Yield: 2.06%
10yr Return: 8.52%
VTI Details
Expense Ratio: 0.03%
Dividend Yield: 1.53%
10yr Return: 12.23%
VT vs. VTI Historical Performance
The VT ETF has a 10-year return of 8.52%, which is lower than the 10-year return of the VTI ETF, which is 12.23%. The VT ETF is a global equity ETF that invests in both U.S. and international stocks, while the VTI ETF is a U.S. equity ETF that invests solely in U.S. stocks. This means that the VT ETF is more diversified and, as a result, may be less volatile than the VTI ETF.
Funds with lower volatility and high diversity will generally outperform in bear markets and underperform in bull markets. Therefore, the VT ETF is a better option if you want to take less risk.
VT vs. VTI Differences
Global vs. US Exposure
The VT ETF provides exposure to both U.S. and international stocks, while the VTI ETF invests only in U.S. stocks. This means that the VT ETF is more diversified and may offer investors exposure to a broader range of companies and industries around the world.
On the other hand, the VTI ETF is focused solely on U.S. companies, which could be an advantage for investors who prefer to invest only in domestic equities.
Expense Ratio
The VT ETF has an expense ratio of 0.07%, which is higher than the VTI ETF's expense ratio of 0.03%. This means that the VTI ETF is less expensive to own and could be a good choice for investors looking to minimize costs.
Index Tracking
The VT ETF tracks the FTSE Global All Cap Index, which includes large, mid, and small-cap stocks from developed and emerging markets. On the other hand, the VTI ETF tracks the CRSP US Total Market Index, which includes all investable U.S. equities, ranging from small to large-cap companies.
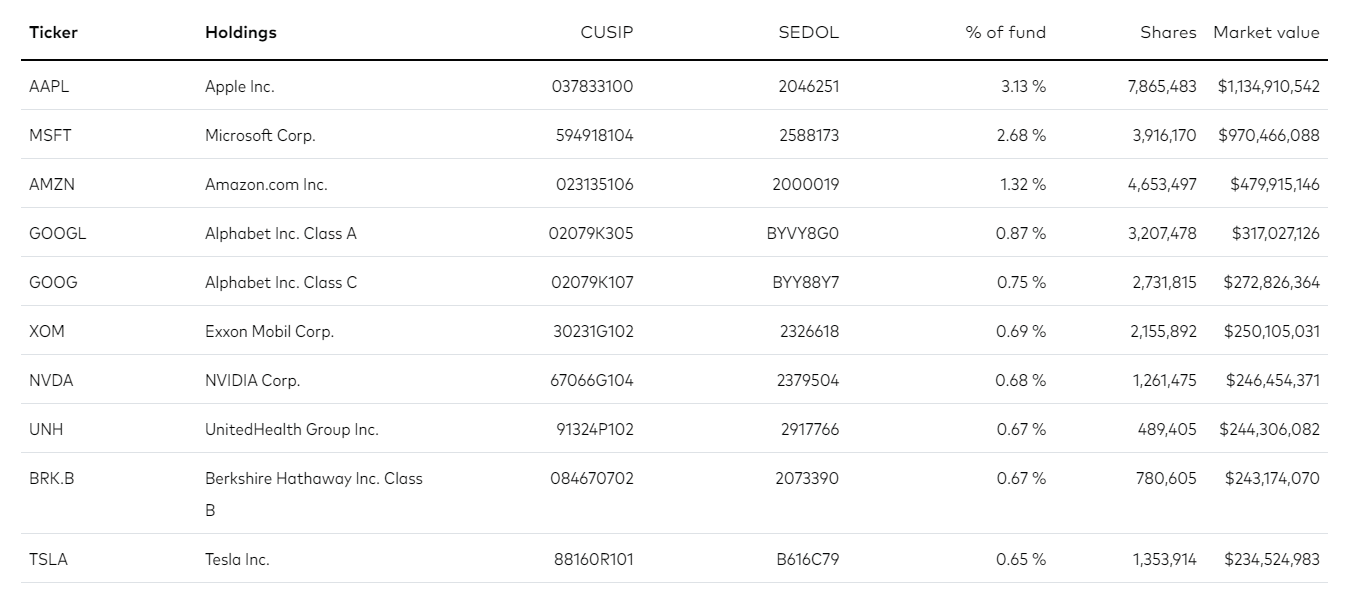
VT Holdings
The top ten VT holdings are all American companies, even though the fund invests in several countries. In addition, 58% of the fund is allocated to American stocks, which is a significant amount. Therefore, it is not an ideal fund if you specifically want international exposure.
VTI Holdings
The top ten holdings of VTI are strikingly similar to VTI as the fund manager believes these strong American companies are the best investments on the stock market. However, VTI is diversified across several sectors but is weighted the most in tech companies.
VT vs. VTI | Which is Best for You?
The main difference between these two ETFs is whether you want foreign exposure. VT is diversified into several countries, while VTI primarily focuses on American companies.
Each fund's top ten holdings are similar, so you are primarily deciding if you want more diversity. VT will be slightly less volatile and will likely weather bear markets better.
Each ETF invests in thousands of companies, so you will have plenty of diversity for a base allocation for a long-term portfolio with either of them.
The Benefits of Diversifying Into Foreign Equities
Diversification is an important investment strategy that can help to reduce risk and improve long-term returns. One way to diversify a portfolio is to invest in foreign equities, which are stocks of companies located outside of an investor's home country.
Reduced Risk
Investing in various assets from different countries can reduce their exposure to risks specific to their home country. For example, if an investor's portfolio is heavily concentrated in U.S. equities, their portfolio could be at risk if the U.S. market experiences a downturn.
However, investors can reduce this risk by investing in foreign equities by spreading their investments across different markets.
Currency Diversification
When investing in foreign equities, investors are also exposed to different currencies. This can provide a hedge against inflation and a diversification of currency risk. If an investor's home currency experiences a decline in value, foreign investments can provide a buffer against this risk.
Global Trends
Investing in foreign equities can also provide exposure to global trends, such as demographic shifts, technological advancements, and geopolitical developments. Investing in companies located in different regions, investors can gain a better understanding of these trends and their potential impact on the global economy.